Going Passwordless! Removing the password effectively removes all password hacks
The core concept of security in the enterprise, as well as elsewhere in society, is identity. Are you who you say you are and do you have a right to be here? When it comes to verifying identity, usernames and passwords are universally used log in to websites and applications.
The main concern with identities in the organization is that they are too complex, too easily compromised and too cumbersome. We have dozens of log-in for a variety of different sites, services, networks, VPNs, servers. Each one of these identities has a different password with different rules. Lowercase, uppercase, special characters, the name of your first family pet, it’s very complicated. Some expire every 30 days, some never expire, some are forgotten. Users are in a constant battle with IT administrators to create a password just simple enough for them to remember. In an effort to make passwords easier to remember, users often reuse passwords which also increases their vulnerability.
The Most Common Password Workarounds
As organizations move their applications and data to the cloud to (1) enable accessibility from anywhere and (2) decrease operating costs, users log in to an increasing number of cloud-based applications with weak passwords.
Many organisations think that the best way to work around the password problem is to require users to manually, or through a password manager, create hard-to-guess, complex passwords for every enterprise account.
However, it is time-consuming and difficult to remember 100 or so characters for every single account. A single sign-on would seemingly help by allowing users to use one password for all logins. But what happens when the password manager provider gets hacked, stolen or the one main password is compromised?
For a start, passwords are too easy to steal and guess. According to cybersecurity report findings, passwords accounted for 29.4% data types exposed in breaches. The number of corporate credentials with plaintext passwords exposed on the Dark Web increased by 429%. Even with organization efforts to increase password security awareness policies, users still continue using a weak password. Reused passwords are still the most vulnerable potential data breaches, accounting for 93.1% of human risk factors. The security findings confirm that organizations need a better, stronger alternative to dangerous password-based security. The answer: passwordless authentication.
What is passwordless authentication?
Passwordless authentication isn’t linked to any specific type of product or technology. The objective of passwordless is to allow users conveniently and securely access applications and services with no passwords to memorize or security question answers to remember.
You may think accomplishing passwordless is more complex than simply using passwords, but in fact, passwordless authentication reduces complexity, while increasing security.
What are Passwordless authentication options available?
Features like multi-factor authentication (MFA) are a great way to secure organization, but users often get frustrated to provide an additional authentication factor, but still may include a password as part of the authentication process and requires to enter security OTP (one Time Password).
Unlike MFA, passwordless authentication may only involve one authentication factor, as long as that factor is not a password. Passwordless authentication methods are more convenient because the password is removed and replaced with possession factors (something the user has eg: hardware token or mobile device) and inherent factors (something the user is eg: facial recognition, fingerprint or PIN).
User identity credentials are stored on the device and never leave it, which makes it much more secure than SMS and time-based 2FA methods, which can be spoofed by hackers. Passwordless method relies on public-key cryptography to authenticate users and never shares any secrets, keeping everything related to a user’s identity private.
The two common forms of passwordless authentications are summarized below.
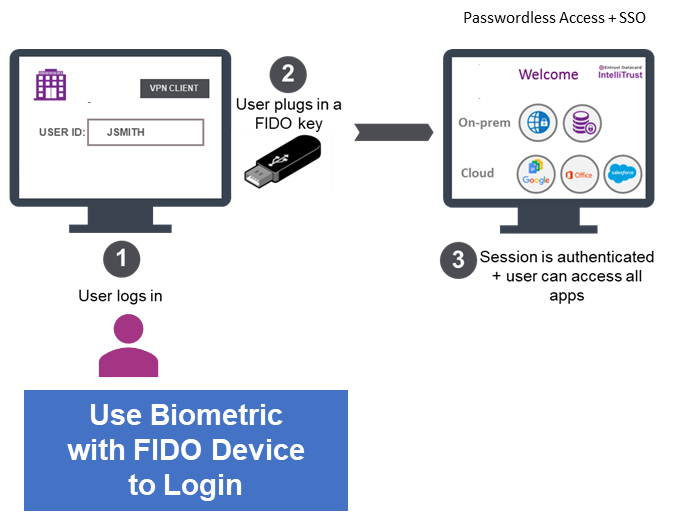
FIDO2 Security Key is a hardware cryptographic device for use with laptops or desktops with Bluetooth and NFC capabilities, expanding the options for quick tap-n-go authentication across desktops, laptops (Windows and MacOS), and mobile devices (iOS and Android).
FIDO2 security key is to replace passwords with public key cryptography to secure the authentication process but does not require a public key infrastructure (PKI). No certificate authorities are required. Some FIDO2 hardware devices are capable of combining PKI smart card & FIDO2 authentication “on the fly” and provide bridge to support applications for both smart card and FIDO2 protocol.
FIDO2 devices are connected to computers via USB, but there are also near-field communication (NFC) and Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) models that can be used for mobile devices. With FIDO2 device, users verify their identity by authenticating with PIN or biometric.
How does FIDO2 work?
To use FIDO2 authentication, users have to register FIDO2 Security Key device with FIDO2 identity service provider. User’s FIDO2 security key device generates a private key and a public key. The public key is stored on the FIDO2 identity service provider and associated with the user’s account to verify users’ identities and encrypt their information. The private key is exclusively stored on users’ FIDO2 devices and used to sign in to authentication challenges and validate users’ identities and decrypt their information.
FIDO2 authentication is done by proving possession of the private key by signing a challenge. The user’s private keys can be used only after they are unlocked by using biometric or PIN to cryptographically sign data that is sent to FIDO2 identity service provider for verification. When users’ private key matches up with public key, they’re granted access to organization resources. Biometric or PIN is stored locally on a FIDO2 device and is therefore highly resistant to the common attacks used against passwords. This approach ensures that the device holders are, in fact, the trusted owners, protecting users’ identities and organization resources.
FIDO2 enables users to securely log in to Windows, macOS and authenticate with a Single Sign On (SSO) using federated identity protocols like SAML or OIDC and access Cloud SaaS Applications like (Salesforce or Microsoft Office 365) using FIDO2 device without requiring password. These include secure access to the following resources:
- Web-based applications, including SaaS applications
- Enterprise applications and technologies
- Operating systems and Active Directory domain-based accounts
- Cloud accounts and services supported by AWS IAM, Azure AD, and Google cloud identity
Mobile Virtual Smart Card is PKI-based passwordless authentication, a digital certificate is issued on a user mobile device (iOS and Android) making it a virtual smart card for authentication, encryption and digital signing. Since the user is authenticated by a PKI-based credential, they can use the same verified identity to send encrypted email, digitally sign documents, and encrypt files.
Virtual smart cards are created in the mobile devices, where the keys that are used for authentication are stored in cryptographically secured hardware. By using mobile devices secure element that provides the same cryptographic capabilities as physical smart cards, virtual smart cards offer comparable security benefits to physical smart cards by accomplishing functionalities of smart cards: non-exportability and isolated cryptography and offer the same physical smart card authentication process experience.
With a Mobile Virtual Smart Card, one device can become the access point for multiple resources eliminating the need to remember many passwords. A user’s mobile phone is always on hand, and by combining the Mobile Virtual Smart Card with biometric security on the device and the strong PKI credentials working silently in the background to validate the secure mobile device. This ensures that the credential holder is, in fact, the credential owner, protecting users’ digital identities and organization resources.
How does Mobile Virtual Smart Card work?
Users register a digital certificate on their mobile device using onboarding service. Users then install a digital certificate on their mobile device as their personal trusted digital Identity.
When users unlock their mobile devices and access their trusted digital identity using biometric (fingerprint or facial recognition) or PIN, they are granted secure access when in close proximity to their work computer (Windows or MacOS) via Bluetooth or NFC and automatically gives them access to the network and their applications with Single Sign On (SSO) for cloud and on-premise applications. This continues while their phone is in Bluetooth or NFC range of their workstation. When they leave their desk with their phone, they go out of range and they are automatically logged out of everything.
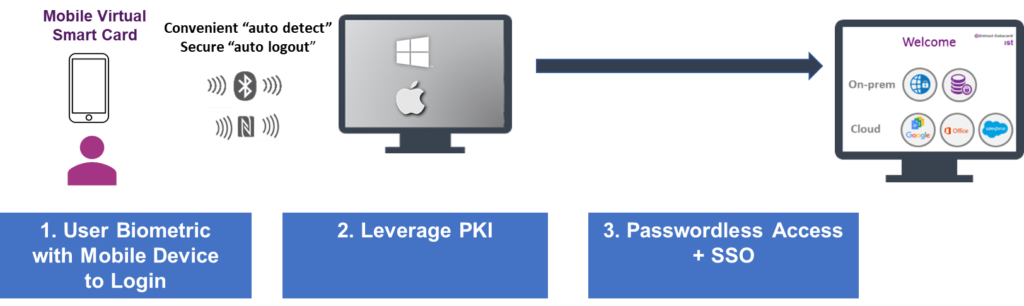
The mobile-embedded identity puts a virtual smart card on the mobile device, using strong PKI to authenticate the device. This approach creates a trusted mobile identity that allows users to authenticate their identities across a wide range of use cases:
- VPN access authentication
- Encrypted email
- Digital signing
- Web app access authentication
- Windows Domain log-on
- Accessing applications using federated identity protocols like SAML, OIDC, or OAuth.
What are the benefits of passwordless authentication?
Improve user experience and productivity. By moving away from long passwords to create, remember and reset, users eliminate the burden to periodically create and remember new passwords, thus ensuring users with a simple tap of fingerprint can get on with their work simply, conveniently and securely access applications and services.
With passwordless authentication, a single mobile device can have different digital identities or single FIDO2 Device can have different private keys for many different sites and applications, so there’s no need for an individual to have multiple mobile devices or FIDO2 devices.
Better Security: Passwordless solution replaces weak passwords with strong hardware-based authentication using public key cryptography and effectively eliminates all password-based threats, including phishing, dictionary, brute force, and credential stuffing. Since passwordless authentication credentials are only accessible with a user biometric or PIN on a user’s device, it is inherently more secure and can’t be inappropriately used by multiple users. As a result, access management becomes tighter.
Reduced total cost of ownership (TCO): Reduce the IT operation costs associated with continuously manage and reset passwords for users, which is time-consuming and expensive to maintain. By replacing passwords with a simple biometric, organisations will reduce support tickets and free IT to deal with real problems.
Closing Thoughts
Identity is critical to today’s organisations, and managing them is clearly a complex task. Organizations need to consider authentication that addresses the current authentication scheme while taking advantage of the technologies that make it more secure, easy to use and cost-effective.
Passwordless identities allow you to move beyond passwords and transform business processes. Passwordless authentication is more secure, more convenient and doesn’t feel burdened to use. Implement Passwordless authentication eliminates the risks associated with weak or stolen passwords while providing a seamless login experience around applications and services.
Is Passwordless authentication right for your organisation needs? That depends on your security priorities. However, we expect it to continue to gain support and adoption with security breaches driving organizations to seek more secure authentication methods.
Embark towards a passwordless authentication today
Contact Netrust Sales Team at sales@netrust.net.


