Passwords have been used for security since the 1970s. Throughout time, they have become the weakest point of security for organizations. Passwords can be easily targeted by online attacks, scams, and other dangers. For a long time, data breaches have been the biggest worry for businesses when it comes to security. The Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report (DBIR) found that 81% of data breaches caused by hacking are a result of passwords that are compromised, weak, or stolen. Identity theft is one of the biggest worries for users. Having long passwords, although they are difficult and irritating to remember, do not offer much protection against password phishing and other cyber-attacks. What actions can the industry take?
The idea of going passwordless comes from trying to make things easier for users. People often forget passwords, write them down, or even share them with others. This can be risky for security. Going passwordless will help solve these problems and make authentication more secure.
Why go passwordless?
Traditional remote authentication method leveraging a username and password
The current “username and password” authentication is:
- Agree on a password, and
- Have the server compare its version – e.g. a hash – with what the user entered.
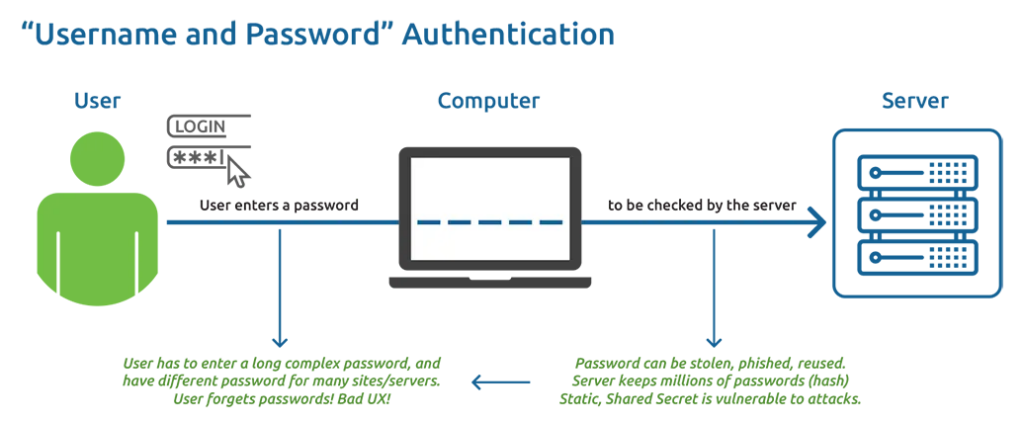
In this situation, attackers can find out your current password by tricking you or using other harmful methods. They can use any device connected to the Internet to log in and access the website, just like you, no matter how hard or strong your passwords are. Using a long and complicated password, and having different passwords for different websites or servers, might make it a little bit harder for attackers to succeed, but it doesn’t make a huge difference. Even though you’ve been trying really hard to remember those passwords without writing them down,
To make sure remote authentication is really safe, newer solutions are designed to prevent attackers from faking it, even if they have access to vast computing power. It would take them millions of years to successfully fake the authentication.
Authentication using public-key cryptography
With public-key cryptography, the person can use their private key to sign certain information. The server can check that the signature is from the user because only the user has the private key. The process of confirming someone’s identity can be done without using a secret code or the person revealing their private key.
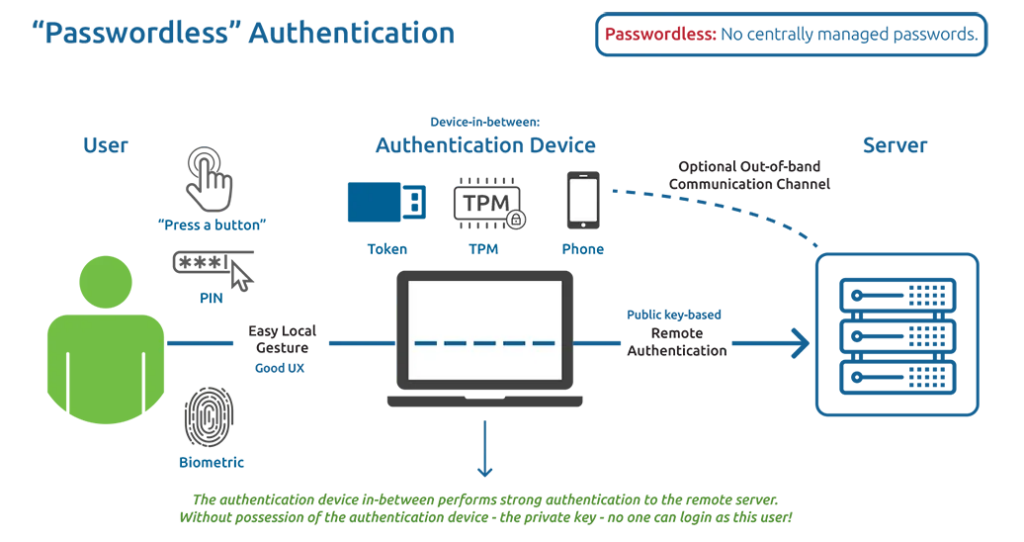
In this situation, we observe:
- In the previous way of logging in with a username and password, the device only helps to connect the user to the server for verification. The password is like the “knowledge” required for MFA.
- The new passwordless solution means that the device now authenticates instead of the user. When we refer to the “user” in the actions involving cryptography, we are talking about the device used for authentication. The device needs to be able to do certain security tasks using special codes, and it also needs to have a special secret key on the server. Because the private key cannot be taken from the device, nobody can prove their identity without it.
- So, this “device” ensures that remote authentication is safe. It is much more secure than the longest and most complicated password, by thousands or even millions of times. If this “device-in-between” could also help you avoid remembering many long, complicated, and different passwords, it would be ideal.
Conclusions
- By using passwordless authentication, the industry’s efforts will probably eliminate identity theft, which is the main cause of online data breaches. Users will not have to deal with lots of long and complicated passwords anymore.
- The way we communicate to confirm who we are is safer when using a computer rather than a smartphone. Not using the smartphone is also easier.
- We are just starting to transition into an era where passwords are no longer used. Some big companies support FIDO on websites and SaaS today, but not all companies do. The companies that sell popular applications, called servers, will soon offer ways to log in without a password. This will be easy to set up because there will be rules in place to make sure it works smoothly between the application, the security system, and the users.
- Now, with endpoint presence and passwordless authentication solutions, encryption and authentication on the endpoint can provide the most user-friendly experience possible.
- The laptop has a special chip called a crypto-chip that helps to keep information secure. This chip can be found in a built-in module called TPM, but even if the laptop doesn’t have TPM, it still has a secure way of running programs. This makes it easier for businesses to transition into a time when passwords are no longer needed, and it requires very little effort.
Embark on Passwordless Authentication today! Contact Netrust Sales Team at sales@netrust.net.
Follow us on LinkedIn for the latest happenings/updates.


